6th Jul 2023
The Race Against Time: Comparing the Decomposition Time of Different Types of Dishes.
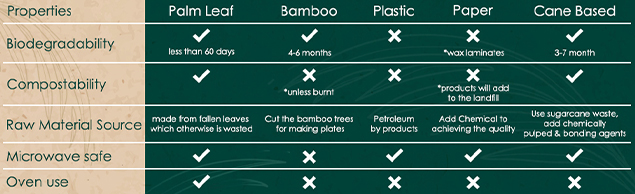
Comparing the Decomposition Time of Different Types of Dishes: Choosing the Sustainable Option
When it comes to the choices we make in our everyday lives, even seemingly insignificant decisions can have a substantial impact on the environment. One such choice is the type of dish ware we use, particularly disposable plates. With the growing concern for sustainability, it becomes crucial to understand the decomposition time of different types of dishes. In this article, we will compare the decomposition time of plastic, paper, palm leaf, bamboo, and cane-based plates, aiming to identify the most environmentally friendly option.

Plastic Plates: Plastic plates, commonly made from polystyrene or polypropylene, have become a staple in our fast-paced, convenience-oriented society. Unfortunately, their durability comes at a significant cost to the environment. Plastic plates take an exceptionally long time to decompose, often ranging from several hundred to a thousand years. This prolonged decomposition period contributes to the accumulation of plastic waste in landfills and oceans, leading to adverse effects on ecosystems.

Paper Plates: Paper plates, while initially appearing more eco-friendly, also have their drawbacks. Typically made from a mix of paper and a thin layer of polyethylene coating for moisture resistance, they have a decomposition time ranging from two to five months. Although paper plates decompose faster than plastic plates, they still contribute to deforestation and require significant energy and resources during production.

Palm Leaf Plates: Palm leaf plates have gained popularity as a sustainable alternative to traditional disposable plates. Made from fallen leaves of the Areca palm tree, they are entirely natural and biodegradable. These plates are produced without harming or cutting down palm trees. Palm leaf plates have an impressive decomposition time of just two months, significantly reducing the burden on landfills and ecosystems. They also offer excellent heat resistance and can be used for both hot and cold foods.

Bamboo Plates: Bamboo plates have garnered attention due to their eco-friendly properties. Bamboo is a fast-growing, renewable resource that requires minimal water and pesticides during cultivation. However, bamboo plates often undergo a manufacturing process involving adhesive binders, which may affect their decomposition time. On average, bamboo plates take approximately six months to decompose, making them a viable option compared to plastic and paper plates

Cane-based Plates: Cane-based plates, derived from sugar cane fiber, are another sustainable choice. Sugar cane is a rapidly renewable resource, and the manufacturing process of cane-based plates involves minimal chemical treatments. These plates have a decomposition time ranging from two to six months, depending on their thickness and environmental conditions. Like palm leaf plates, cane-based plates are biodegradable and suitable for hot and cold foods.
In conclusion, considering the decomposition time of different types of dishes, palm leaf plates seem to be the best option for reducing environmental impact. They decompose in just two months, significantly faster than plastic, paper, bamboo, and cane-based plates.
By choosing palm leaf plates, you not only contribute to a cleaner environment but also enjoy the natural beauty and sturdiness they offer. Explore our wide range of eco-friendly tableware options and make the switch to sustainable dining with Planet Pantry.In our next article, we will explore how to properly decompose palm leaf plates to make fertilizer, highlighting the multiple benefits of using this eco-friendly alternative in everyday life. By making conscious choices like opting for palm leaf plates, we can contribute to a more sustainable future.
Explore how to properly decompose palm leaf plates to make fertilizer.



